Deoxyribo Nucleic Acid more stable double stranded form that stores the genetic blueprint for cells the sugar is Deoxyribose RNA?RiboNucleicAcidis a more versatile single stranded form thatDeoxyribose replaces the 2'hydroxyl group found in RNA with a hydrogen;
What Are The Three Parts Of A Nucleotide Albert Io
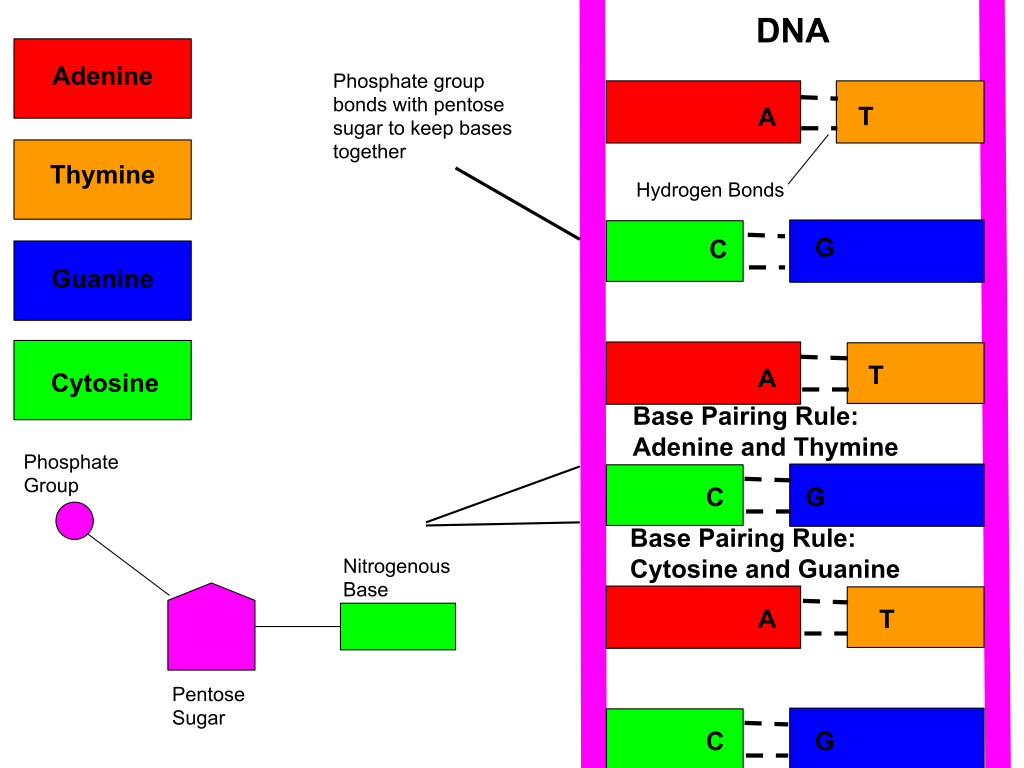
Double stranded dna structure is composed of pentose sugars phosphate groups and nitrogenous bases
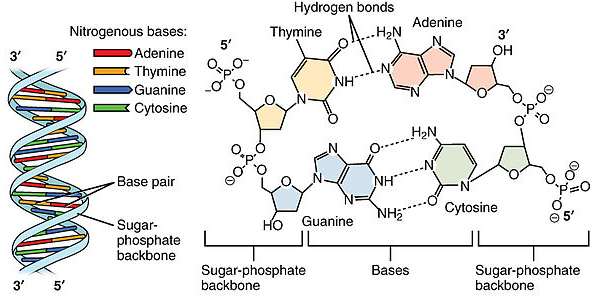
Double stranded dna structure is composed of pentose sugars phosphate groups and nitrogenous bases- · The structure of DNA DNA is a double helix structure because it looks like a twisted ladder The sides of the ladder are made of alternating sugar (deoxyribose) and phosphate molecules while the steps of the ladder are made up of a pair of nitrogen bases As a result of the double helical nature of DNA, the molecule has two asymmetric groovesEach of the sugar groups in this sugarphosphate backbone is linked to one of the four nitrogenous bases Strand of polynucleotides DNA's ability to store and transmit information lies in the fact that it consists of two polynucleotide strands that twist around each other to form a doublestranded helix The bases link across the two strands in a specific manner using



Lesson Explainer Dna Discovery And Structure Nagwa
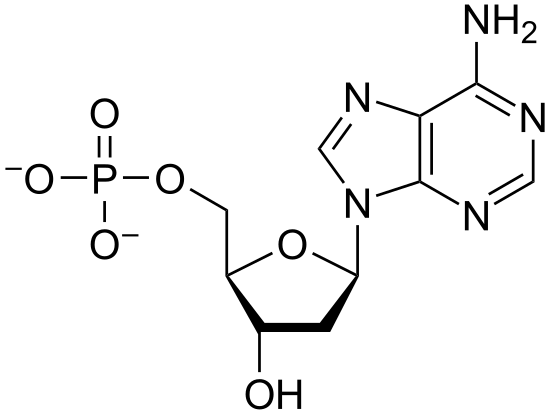
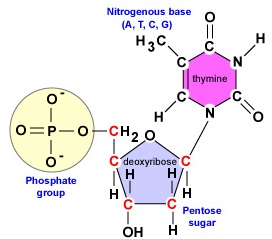
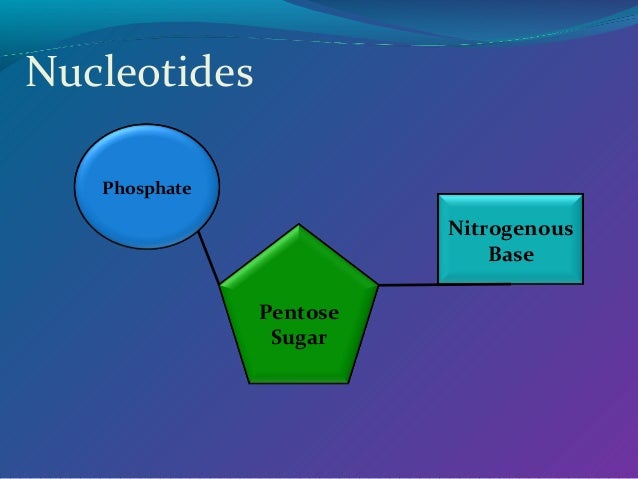
Nucleotide Structure Nucleic acids are long chains (polymers) of lots of nucleotide monomers joined together by phosphodiester bondsEach nucleotide is made up of three components a pentose sugar (either deoxyribose or ribose), a nitrogenous base (guanine, cytosine, adenine, thymine or uracil) and a phosphate groupDNA consists of two nucleic acid strands bondedIt was isolated from pus (leukocytes) from bandages; · One, two or three phosphate groups can be attached to the pentose sugar, producing mono, di and triphosphates respectively Pentose sugar used by DNA is deoxyribose and the pentose sugar used by RNA is ribose Nitrogenous bases found in DNA are adenine, guanine, cytosine and thymine In RNA, thymine is replaced by uracil
Doublestranded DNA molecule (Questions 116) 11_____ Which structural feature is found in the singlestranded DNA molecule?A) It can have a negativelycharged backbone composed of nitrogenous bases b) Each 3',5'phosphodiester bond will contain one phosphate group linking two deoxyribose sugars c) It can have one end with a 5'phosphate group while the other endAn interesting notable fact is that ten (10) base pairs are present in one helix or turn, of the doublestranded DNA A pentose sugar molecule to which the nitrogenous bases are attached at the first carbon (1') and the phosphate molecule, the third main component of
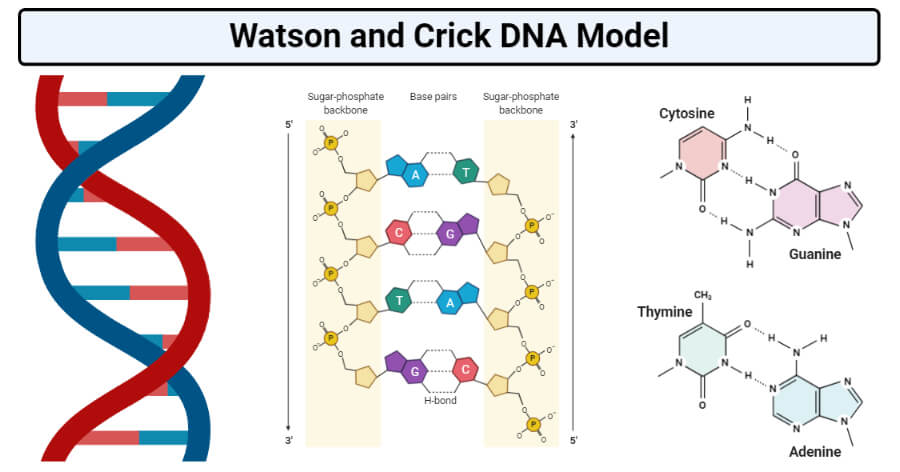
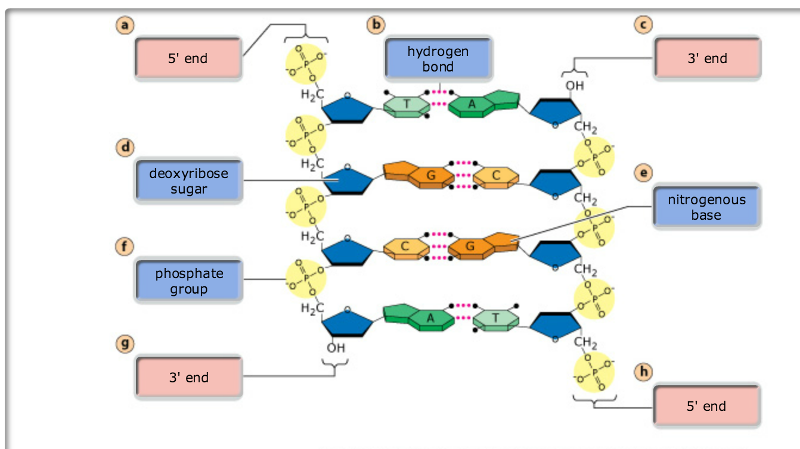
The structure of DNA was first identified as having a 'doublehelix' structure by Watson and Crick in 1953 DNA is composed of 4 bases the purines, adenine (A) and guanine (G) and pyrimidines, thymine (T) and cytosine These form complementary base pairs of AT and GC DNA also contains a phosphate group connected to a deoxyribose sugarDNA double helix has Phosphatesugar backbone The backbone of DNA double helix is made by the sugar and phosphate molecules The polynucleotide chains in DNA are arranged in such a way that the sugar and phosphate molecules are arranged on the outer side of the double helix with the nitrogenous bases facing inwards 5 The two chains are held together by hydrogen bondsDNA Deoxyribose is the pentose sugar found in this type of polynucleotide, hence its name Deoxyribonucleic Acid, or DNA The nitrogenous bases found in DNA are, adenine, guanine, cytosine and thymine DNA molecules have two polynucleotide chains, held together in a ladderlike structure The sugar phosphate backbones of the two chains run parallel to each other in


Nucleotide Wikiwand



Nucleic Acids Genetics Learnbiology Net
Concept of DNA 2 Structure of DNA 3 Unusual Bases 4 Replication Concept of DNA DNA is present in the cells of all plants, animals, prokaryotes and in a number of viruses In eukaryotes (eg, Escherichia coli, a bacterium) the genetic material consists of a single giant molecule of DNA about 1,000 microns in length, without any associated proteins DNA is present mainly in theDNA is a two stranded molecule whose shapes resembles a double helix Nucleotides are the Building Blocks DNA (and RNA) are made up of monomers called nucleotides Each individual nucleotide is made up of three components (i) a nitrogenous base (ii) a pentose (fivecarbon) sugar, and (iii) a phosphate groupLinked nucleotides are the phosphatesugar backbone of nucleic acids, and their nitrogenous bases extend from this phosphatesugar backbone like teeth of a comb The Nucleic Acid "Ladder" In DNA, hydrogen bonds form between specific bases of two nucleic acid chains, forming a twisted, doublestranded DNA molecule that looks like a spiral staircase, with the two sugarphosphate


Difference Between Dna And Genes Definition Structure Features Comparison



S16 Bis2a Lecture17 Reading
The nucleotide is the elementary unit of nucleic acids They composed of nucleosides and phosphate group A nucleoside is composed of a nitrogen base and pentose sugar Pentose sugars are ribose and deoxyriboseAs you know that nucleic acid are giant molecules having complex structure and very high molecular weight, it contains two types of nitrogenous bases double ring purines and single ringed pyrimidine and two types of Pentose sugars ribose and deoxyribose, it store and transfer information needed for the synthesis of specific proteins that determine the structure andIn the nucleus, DNA is always found as a doublestranded molecule This means that one DNA molecule consists of two DNA strands Each strand is made up of a DNA backbone (the phosphate groups and the pentose sugars) and the bases


h5425 Molecular Biology And Biotechnology



Atp Learn Biochemistry
This video explains The Pentose Sugars { Ribose & Deoxyribose } and the Nitrogenous bases present in Nucleic Acids along with the Structure of DNA proposed bIn a nucleotide molecule, a nitrogenous base and a phosphate group attached to a pentose sugar In this case, one to three phosphate groups can be attached to the 5′ carbon of the pentose sugar The purine (adenine and guanine) and pyrimidine (cytosine, uracil, and thymine) are the nitrogenous bases Nucleotide = Sugar Base PhosphateDNA was isolated in 1869 by Friedrich Miescher ;



Nitrogenous Base An Overview Sciencedirect Topics


Nucleic Acids Mhcc Biology 112 Biology For Health Professions
Nucleic acids are composed of nucleotides, each of which contains a pentose sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base Deoxyribonucleotides within DNA contain deoxyribose as the pentose sugar DNA contains the pyrimidines cytosineThe backbone of DNA is based on a repeated pattern of a sugar group and a phosphate group The full name of DNA, deoxyribonucleic acid, gives you the name of the sugar present deoxyribose Deoxyribose is a modified form of another sugar called ribose I'm going to give you the structure of that first, because you will need it later anywayHe termed the substance nuclein;


Ch02 Nucleic Acids And Atp



What Are The Three Parts Of A Nucleotide Albert Io
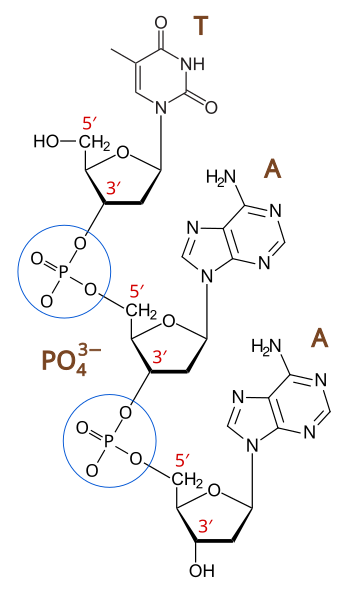
The purines are adenine and guanine Both strands of doublestranded DNA store the same biological information This information is replicated as and when the two strands separate A large part of DNA (more than 98% for humans) is nonThe phosphodiester bonds link the pentose sugar to the phosphate resulting in the sugarphosphate backbone Since the nitrogenous bases do not take part in the polymerisation, the sugarphosphate backbone is made and the nitrogenous bases extending out from it A polynucleotide has a free phosphate group at one end, this end is called the 5' end (because the phosphateThe nucleotides are covalently linked together in a chain through the sugars and phosphates, which thus form a "backbone" of alternating sugarphosphatesugarphosphate (see Figure 43) Because only the base differs in each of the four types of subunits, each polynucleotide chain in DNA is analogous to a necklace (the backbone) strung with four types of beads (the four bases



Storing Genetic Information Biology For Non Majors I


Structure Of Nucleic Acids Nucleotides And Nucleic Acids Sparknotes
DNA molecules are made up of two polynucleotide strands lying side by side, running in opposite directions – the strands are said to be antiparallel Each DNA polynucleotide strand is made up of alternating deoxyribose sugars and phosphate groups bonded together to form the sugarphosphate backboneThe nitrogenous bases of each nucleotide project out from the backbone towards the interior of the doublestranded DNA molecule;And the phosphate of the next nucleotide These strong bonds form a sugarphosphate backbone The ends of the DNA strand are called the 5' end (said as "5 prime end") at the phosphate


What Is The Backbone Of Dna Made Of Quora



Nucleotides Bioninja
· DNA or deoxyribonucleic acid is the substance of chromosomes which form the genetic material in almost every living organism It is a helical (twisted around itself) doublestranded structure made up of nucleotides comprising a · Nucleotide A nucleotide is a structure made up of pentose sugar, a nitrogencontaining base (nitrogenous base) and phosphate The nucleotide is a structural building block of DNA Each nucleotide joint with the nucleotide of another strand with the hydrogen bond and other adjacent nucleotides with the phosphodiester bondThe complementary nitrogenous bases are divided into two groups, pyrimidines and purines In DNA, the pyrimidines are thymine and cytosine;


Principles Of Biochemistry Nucleic Acid I Dna And Its Nucleotides Wikibooks Open Books For An Open World



Deoxyribonucleic Acid The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary
Nucleic acids are composed of nucleotides, each of which contains a pentose sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base Deoxyribonucleotides within DNA contain deoxyribose as the pentose sugar DNA contains the pyrimidines cytosine1 A molecule of DNA consists of two strands that form a double helix structure DNA is a macromolecule consisting of two strands that twist around a common axis in a shape called a double helixThe double helix looks like a twisted ladder—the rungs of the ladder are composed of pairs of nitrogenous bases (base pairs), and the sides of the ladder are made up of alternating sugarAlternating sugar and phosphate units form the two sides of a laddershaped arrangement with the rungs or steps each formed by a pair of nucleotide bases Figure 2 below shows the structural formula of DNA in greater detail The nitrogen bases are ring compounds with their carbon and nitrogen atoms arranged in single or double rings Only certain bases can pair together to form



2 6 Dna Rna Structure
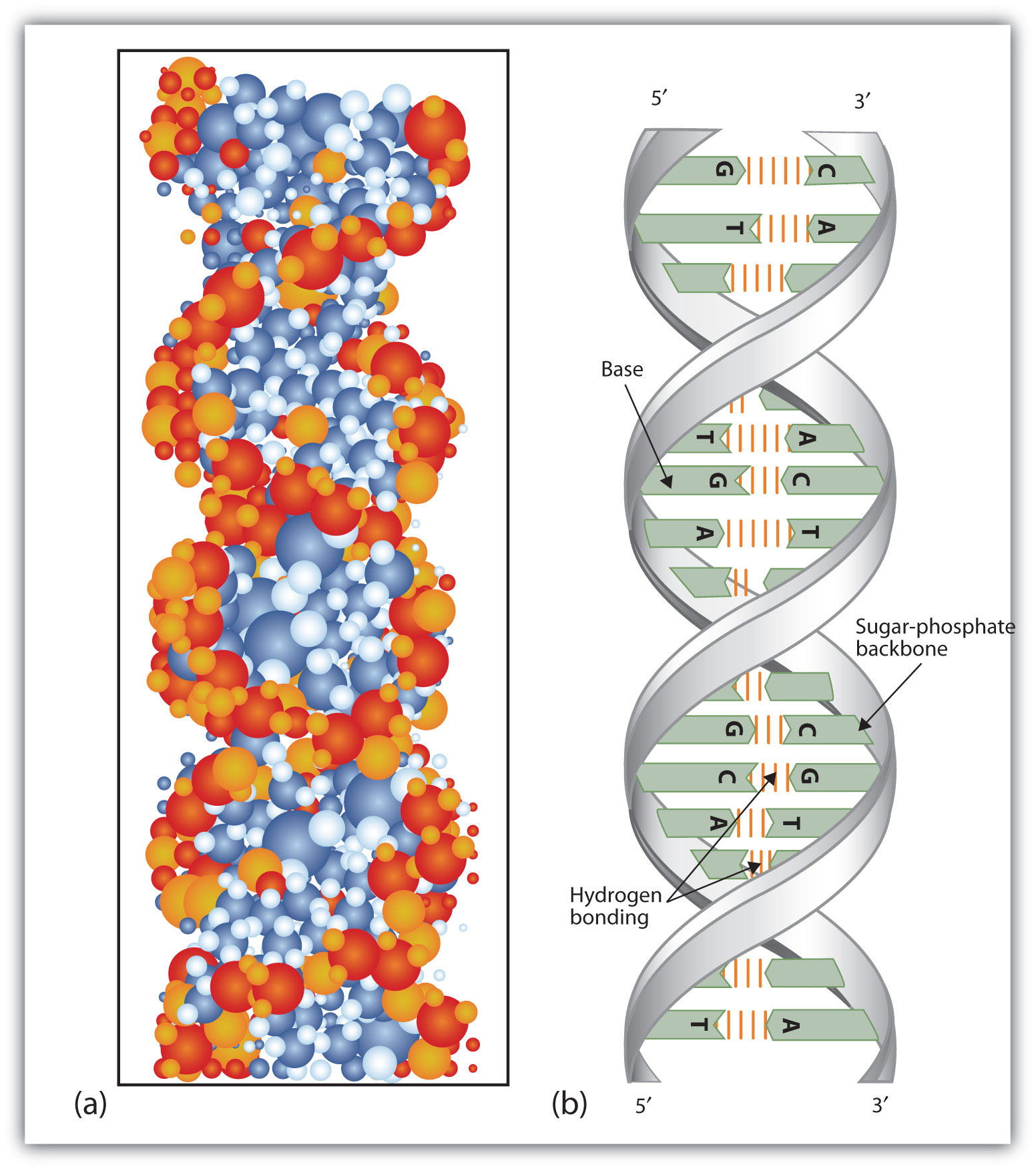


Nucleic Acids
Double helix is the description of the structure of a DNA molecule A DNA molecule consists of two strands that wind around each other like a twisted ladder Each strand has a backbone made of alternating groups of sugar (deoxyribose) and phosphate groups Attached to each sugar is one of four bases adenine (A), cytosine , guanine (G), or thymine (T) The two strands are held · Genomic DNA is a double helix structure that is composed of several components including purines (adenine and guanine) and pyrimidines (cytosine and thymine) as nitrogenous bases, deoxyribose sugar (a pentose sugar) and phosphate groupsIt is a large nucleic acid molecule composed mainly of two polynucleotide chains or strands that are coiled in a complementary fashion to form a doubleNitrogenous base Phosphate base both attached to the central pentose sugar DNA?
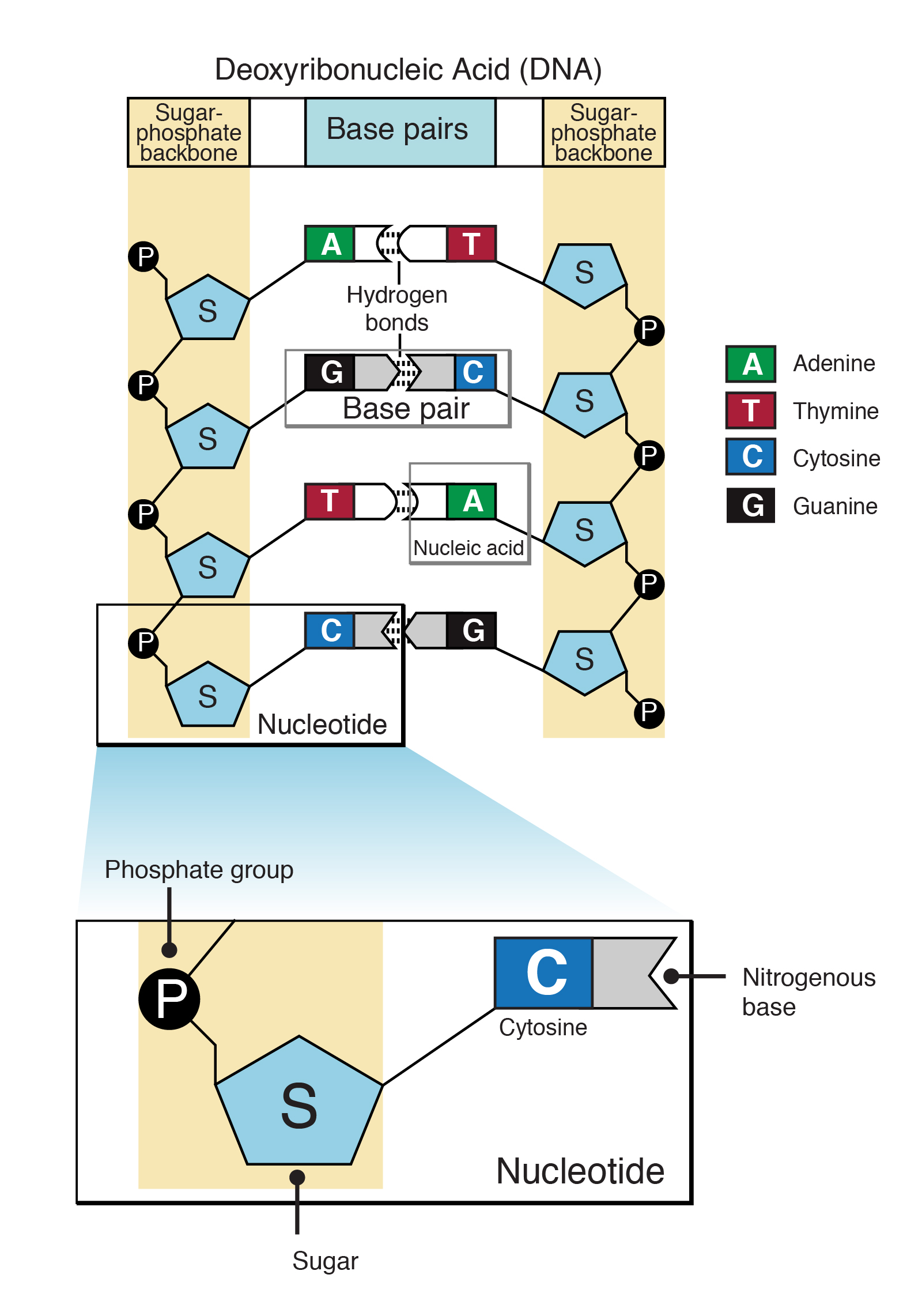


Nucleotide



Nucleic Acids Dna Rna What Do They Do
DNA and RNA A nucleotide is made up of three components a nitrogenous base, a pentose sugar, and one or more phosphate groups Carbon residues in the pentose are numbered 1′ through 5′ (the prime distinguishes these residues from those in the base, which are numbered without using a prime notation) The base is attached to the 1′ position of the ribose, and the phosphateFinally, we will describe the doublestranded structure of dsDNA 1 The monomers are "nucleotides" three components Pentose (5 carbon) sugar either ribose (RNA) or deoxyribose (DNA) The carbons are numbered clockwise The difference between the sugars is that ribose has an OH group on the 2' carbon, whereas deoxyriboes has only 2 H groups and thus isDNA is made up of two strands of nucleotides, which include a phosphate group, five carbon sugar, and a nitrogenous base Each individual strand in held together by strong covalent bonds (a bond formed as a result of the distribution of electrons between atoms) The two strands are then joined to each other by hydrogen bonds between complementary bases There are four nitrogenous bases



Dna Vs Rna 5 Key Differences And Comparison Technology Networks



Nucleotides Types Examples Functions Classification
· A DNA molecule has two long polynucleotide chains coiled into a double helix structure Hence, DNA exists as a doublestranded highly coiled helix Each nucleotide has three components a phosphate group, a deoxyribose sugar, and a nitrogenous base (adenine, thymine, cytosine or guanine) Figure 01 DNA Eukaryotes store most of their DNA inside the nucleus while prokaryotes store their DNA · Nucleotides are composed of a pentose sugar molecule, a nitrogenous base, and a phosphate group These make up one nucleotide monomer which, when combined into a polymer, can create nucleic acids, DNA or RNA Each nucleotideis made up of three components · Each nucleotide subunit is composed of a pentose sugar (deoxyribose), a nitrogenous base, and a phosphate group The two strands associate via hydrogen bonds between chemically complementary nitrogenous bases Interactions known as "base stacking" interactions also help stabilize the double helix
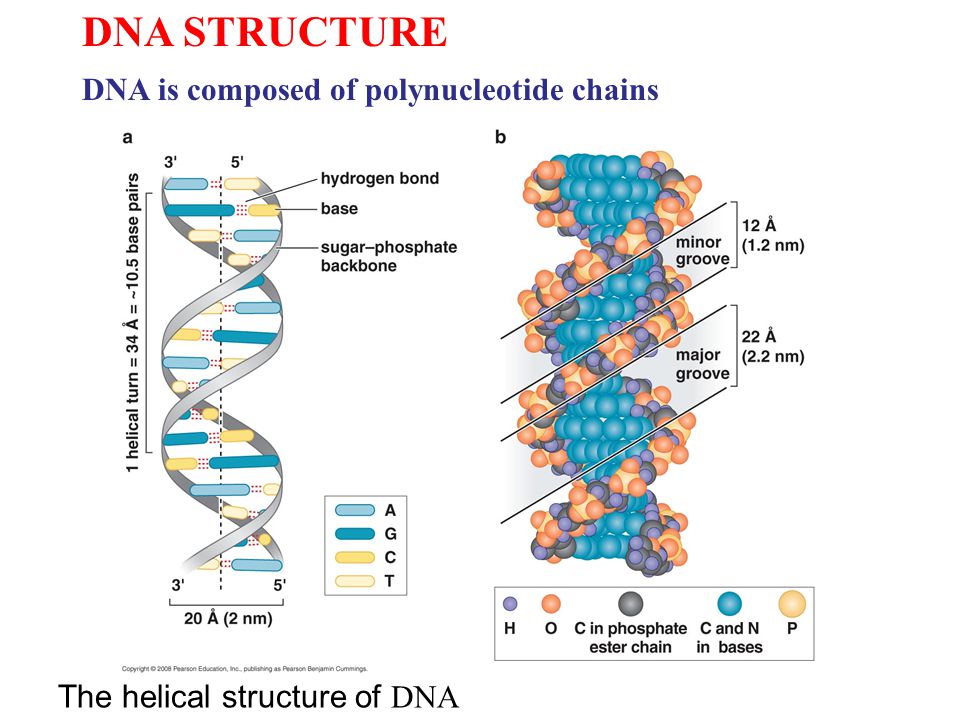


Dna Structure Dna Is Composed Of Polynucleotide Chains Ppt Video Online Download



Doc Dna Rna Function Comparison Roma Pandey Academia Edu
5 carbon pentose sugar phosphate group nitrogenous base Diagram of single nucleotide?B the bases are on the inside of the helix, inaccessible to the UV light in doublestranded DNA C in singlestranded DNA the bases are not interacting so more photons can be absorbed by the pentose rings D singlestranded DNA actually absorbs more of the UV light, making less light available to doublestranded DNA · A DNA molecule is composed of two strands Each strand is composed of nucleotides bonded together covalently between the phosphate group of one and the deoxyribose sugar of the next From this backbone extend the bases The bases of one strand bond to the bases of the second strand with hydrogen bonds


Nucleic Acids Dna Deoxyribonucleic Acid Rna Ribonucleic Acid
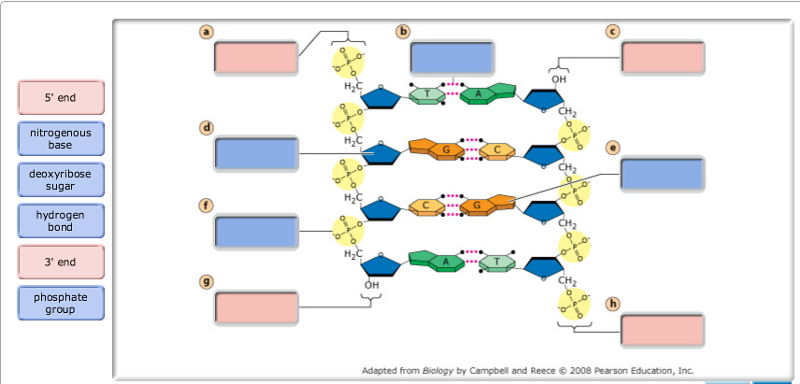


Exam 3 Chs 5 Dna Structure And Replication Machinery 16 The Molecular Basis Of Inheritance Flashcards Easy Notecards
· Structure DNA consists of two strands, arranged in a double helix These strands are made up of subunits called nucleotides Each nucleotide contains a phosphate, a 5carbon sugar molecule and a nitrogenous base RNA only has one strand, but like DNA, is made up of nucleotides RNA strands are shorter than DNA strands RNA sometimes forms aNucleic acid is derived from that term;A single DNA polynucleotide strand showing the positioning of the ester bonds Hydrogen bonding The two antiparallel DNA polynucleotide strands that make up the DNA molecule are held together by hydrogen bonds between the nitrogenous bases;



What Are Nucleic Acids Structure Function Expii



Nucleotide High Res Stock Images Shutterstock
· They are composed of phosphate groups, nitrogenous bases and pentose sugars Nucleotides link together by phosphodiester bonds to form polynucleotide chains Nucleic acid is a polymer made up of polynucleotide chains There are two main types of nucleic acids named DNA and RNA DNA is essential for storing and transferring genetic information while RNA is essential



What Is The Chemical Makeup Of Dna Quora


Print Page


The Structure Of Dna



Shutterstock Puzzlepix


Dna Structure


19 3 Deoxyribonucleic Acid Dna Biology Libretexts


Dna And Molecular Genetics


Dna Structure



Structure Of Nucleic Acids Biology For Non Majors I
/what-are-the-parts-of-nucleotide-606385-FINAL-5b76fa94c9e77c0025543061.png)


3 Parts Of A Nucleotide And How They Are Connected


Watson And Crick Dna Model Molecular Biology Microbe Notes


9 1 The Structure Of Dna Concepts Of Biology 1st Canadian Edition



What Are Nucleic Acids Protocol



Find A Diagram Photo Or Other Illustration Of A Dna Molecule Identify The Following In Your Picture Sugar Phosphate And 2 Of 4 Nitrogen Bases Study Com


Exam 3 Chs 5 Dna Structure And Replication Machinery 16 The Molecular Basis Of Inheritance Flashcards Easy Notecards



Dna 2 6 1 The Nucleic Acids Dna



Lesson Explainer Dna Discovery And Structure Nagwa
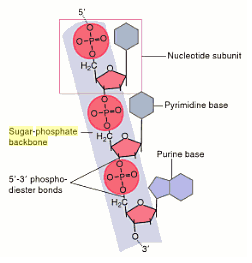


Sugar Phosphate Backbone The School Of Biomedical Sciences Wiki
/DNAstructure-58c233583df78c353c23dbe6.jpg)


Nucleic Acids Function Examples And Monomers



Nucleotides Dna And Rna Amboss


Dna Structure
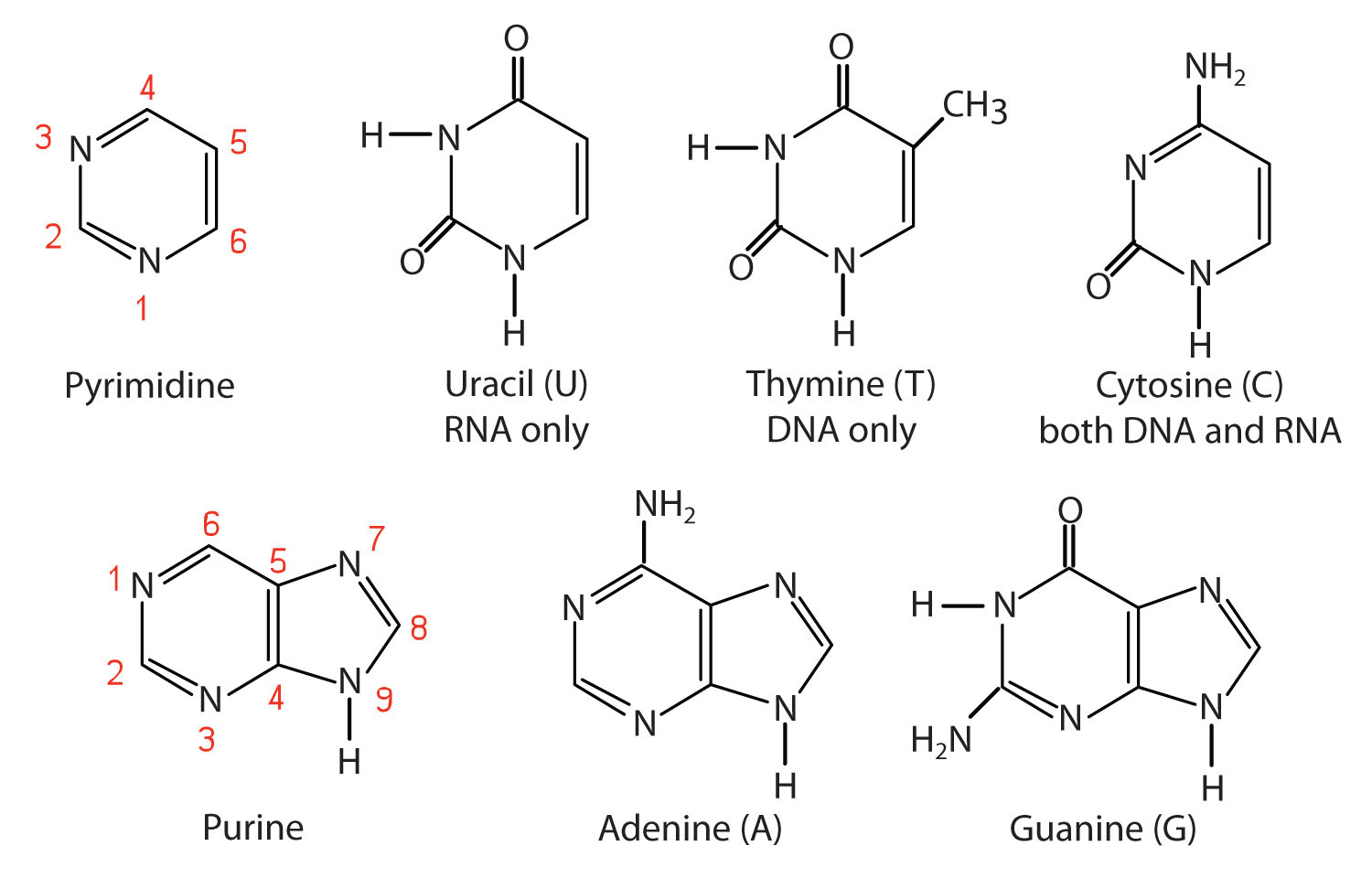


Nucleic Acids
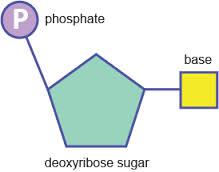


Topic 2 6 Structure Of Dna And Rna Amazing World Of Science With Mr Green



Dna Wikipedia
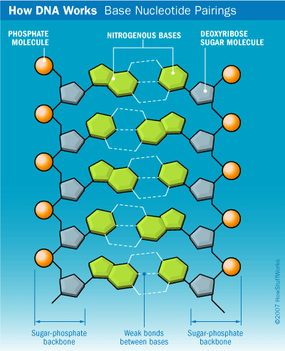


Dna Structure Howstuffworks



Structure And Function Of Dna Microbiology



Nucleic Acid Advance



Nitrogenous Base An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
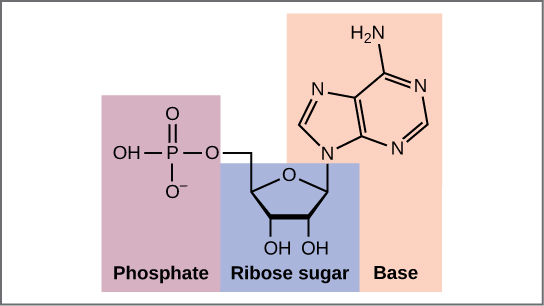


9 1 The Structure Of Dna Concepts Of Biology 1st Canadian Edition



Lesson Explainer Dna Discovery And Structure Nagwa
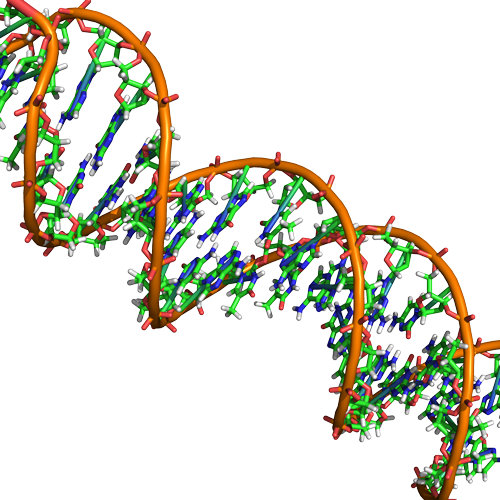


4 4 Nucleic Acids Biology Libretexts


Life Sciences Cyberbridge
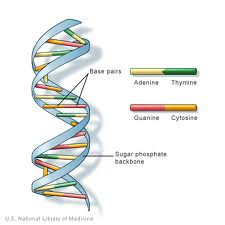


Dna The School Of Biomedical Sciences Wiki



Nucleic Acid Definition Function Structure Types Britannica



Nucleotides And Nucleic Acids The Science Hive



Nucleic Acid Definition Function Structure Types Britannica
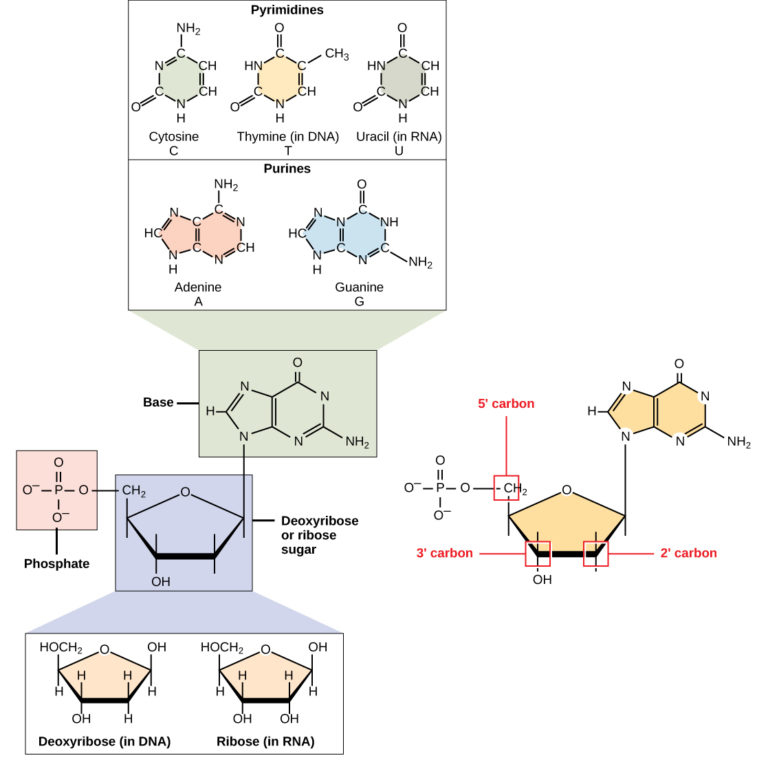


Structure Of Nucleic Acids Biology For Majors I



Nucleotides And Nucleic Acids The Science Hive
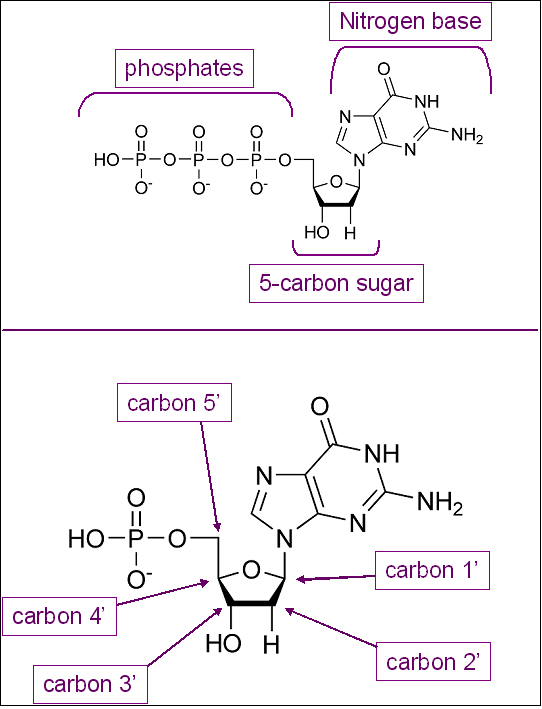


Dna Ii Biology Visionlearning
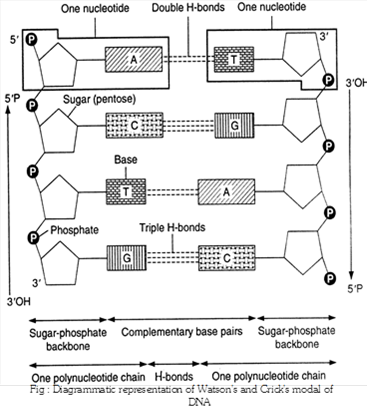


Jee Main Jee Advanced Cbse Neet Iit Free Study Packages Test Papers Counselling Ask Experts Studyadda Com


Ch02 Nucleic Acids And Atp



Nucleotides



2 6 Dna Rna Structure



Structure And Synthesis Of Nucleic Acids And Protines



Unit 3 Nucleic Acids And The Central Dogma Flashcards Quizlet


Print Page



Solved I Really Need Help This Is The Best My Camera Can Chegg Com



Structure And Function Of Dna Microbiology
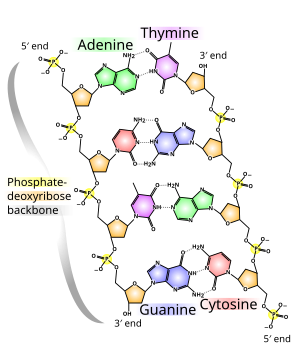


Dna Wikipedia



Chapter 13 Molecular Basis Of Inheritance Flashcards Quizlet
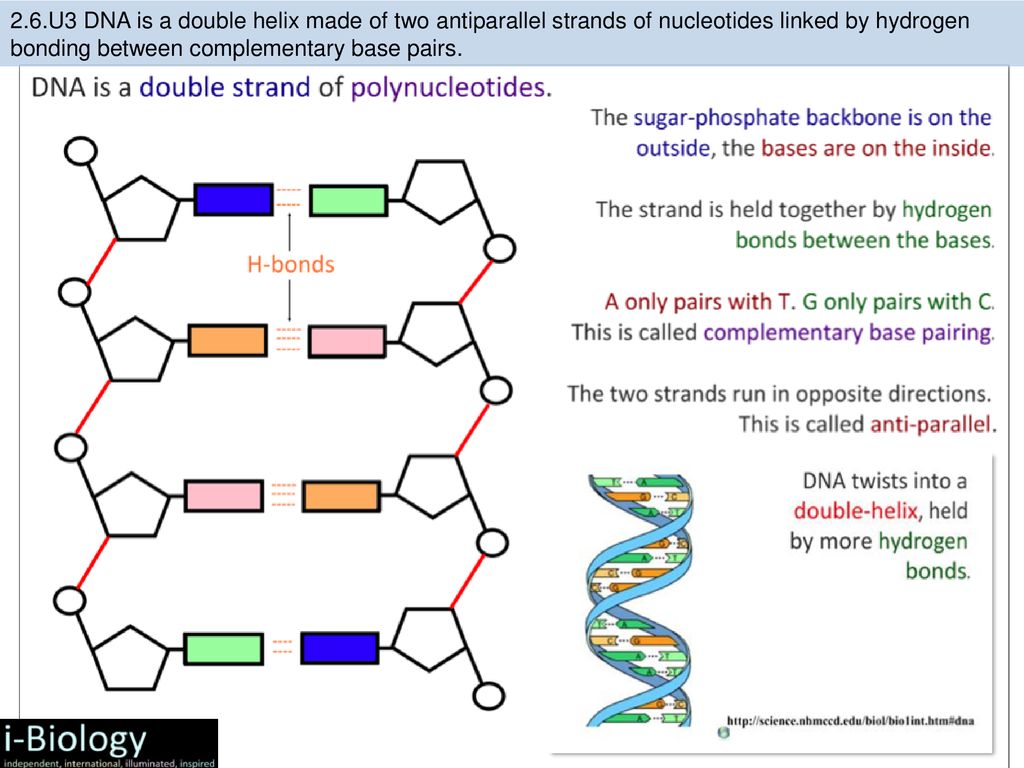


2 6 Structure Of Dna And Rna Ppt Download



Dna And Rna Structure Function Expii



Nucleic Acid



4 4 Nucleic Acids Biology Libretexts



Nucleotides Bioninja



Deoxyribose An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



Dna And Rna Structure Notes Studocu


Difference Between Dna And Mrna Difference Between



Dna Function Structure With Diagram Article Khan Academy



What Are The Three Parts Of A Nucleotide Albert Io
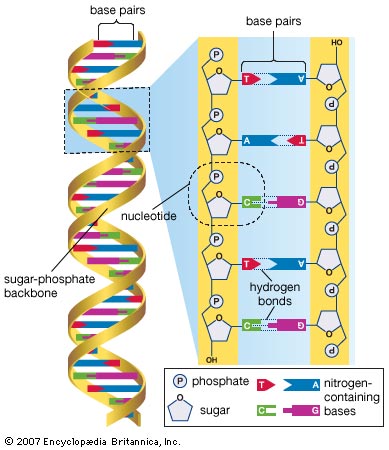


What Is Dna Example



Principles Of Biochemistry Nucleic Acid I Dna And Its Nucleotides Wikibooks Open Books For An Open World



Nucleotide Wikipedia
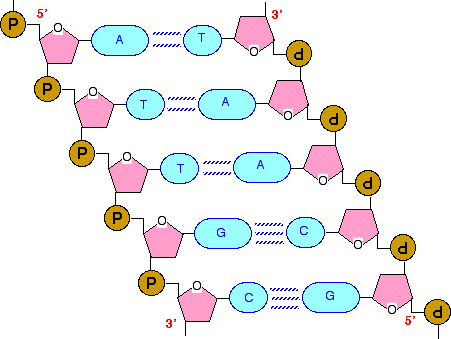


Dna Structure
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/DNA_nitrogenous_bases-5b63374b46e0fb00250bcaa1.jpg)


Nucleic Acids Function Examples And Monomers



Nucleotides Types Examples Functions Classification



Structure And Function Of Rna Biotechnology Fundamentals 2nd Edition Openstax Cnx


What Are The Molecules That Make Up Dna Quora
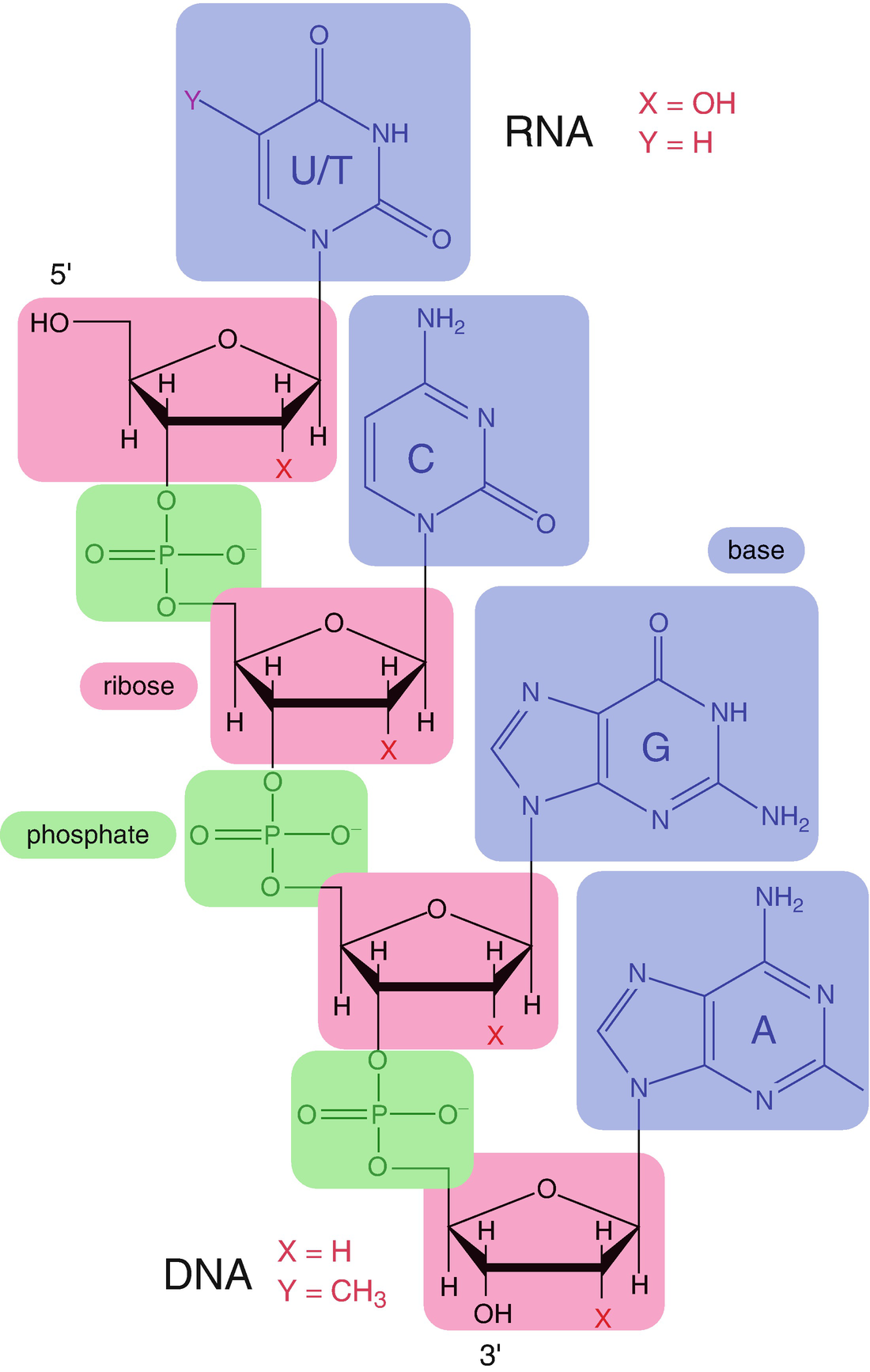


Nucleic Acids Springerlink



Nucleic Acid



Unit 3 Nucleic Acids And The Central Dogma Flashcards Quizlet
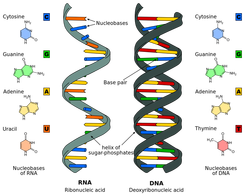


Topic 2 6 Structure Of Dna And Rna Amazing World Of Science With Mr Green



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿